MODULE 1
AT INDERA SEGARA HALL
7/6/2017
GETTING READY TO
LEARN
BY:PROF MADYA DR
HALIL
BIN PAINO
Course
Information
Course : Study Skills
Level : Diploma
Credit Unit : -
Contact Hour : 2
Part : 1 (Interim)
Course Status : Non-core
Prerequisite : None
Syllabus
Content
1.
Getting
Ready To Learn
·
Making the
transition (from school to university)
·
Characteristics
of successful students
·
Using learning
styles to enhance performance
2. Memory, Learning
& Improving Concentration
·
Understanding
memory process
·
Memory
strategies
·
Understanding
concentration
·
Strategies for
improving concentration
·
Reading
procrastination
3.
Taking
Lecture Notes
·
Taking lecture
notes
·
Effective
note-taking system
4.
Academic
Integrity & Performance
·
Avoiding
Plagiarism
·
Calculating
grade point average
5.
Goal
Setting
·
Setting goals
for the new semesters
·
Writing
effective goal statements
·
Using the Learning
Management System
6.
Library
& Campus Resources
·
Using the
resources in the library
7.
Time
Management & Organizational Skills
·
Optimising study
time
·
Organising study
time
·
Using
time-management strategies to stay motivated
·
Reducing
procrastination
This e-portfolio provides 100 marks
and it divided by two:
·
60%
for my e-portfolio by doing at blog or google plus
·
40%
for my group video about 10 persons in group
·
Has
no final exam
·
It
must be submit 7th week
Every week ,I’ll go to the different
venues where the UED 102 class held and we discuss about varieties of topic and
activity.
·
Week
1:Dewan Indera Segara
·
Week
2:Dewan Al-Farabi
·
Week
3:Al-Biruni 1
·
Week
4:Dewan At-Tabari
·
Week
5:Dewan Kuliah 2
·
Week
6:Dewan Ibn Hazm
·
Week
7:Perpustakaan Al-Bukhari
CHARACTERISTIC
OF SUCCESSFUL STUDENT
LEARNING STYLES
TO PERFOMANCE
LEARNING SYLES
·
In
my opinion,it refers to the preffered way that you acquire,process and retain
information the way you learn best.
LEARNING STYLE INVENTORY
·
If I
were preparing for an exam,I’rather listen to asummary I made than a summary for a chapter.
·
I
prefer someone explain how to make a model for a class project than rely on
written directions.
·
I
prefer to practice by reciting out loud when I learn spelling and vocabulary.
MAKING
TRANSITION FROM SCHOOL TO UNIVERSITY
Required
items
1. Learning
Style Inventory
2. Goal
statements – The Five Step Approach
3. Notes
On Library Tour
4. Fixed-Commitment
Calendar
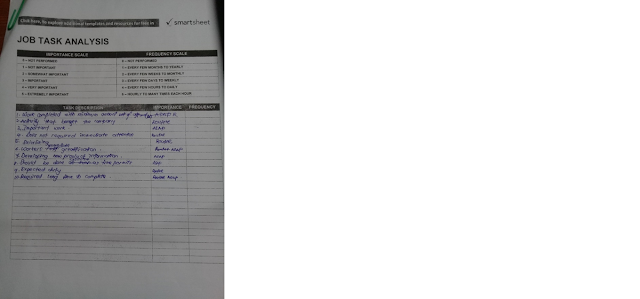
5. Job
Task Analysis
6. Prioritized
To-do List
7. Memory
strategies (Activity 4-1: Van Blerkom, 2009, pg 90
8. Organizational
strategies (Activity 4-7: Van Blerkom, 2009, pg. 107) –optional
9. Concentration
Strategies (Activity 6.1: Van Blerkom, 2009, pg. 144
10. Concentration
Chart (Figure 6.4: Van Blerkom, 2009, pg. 161)
11. Reading
Text (Figure 12.3: Van Blerkom, 2009, pg.309)
12. Note-Taking
Strategies (Activity 5.1: Van Blerkom, 2009, pg. 116)
13. Note-taking
Exercise using the Cornell Method
14. GPA
Worksheet
MODULE 2
AT AL-FARABI
HALL
14/6/2017
TIME
MANAGEMENT & ORGANIZATIONAL SKILLS
BY:DR.MOHAMMAD
AZMI NIAS BIN
AHMAD

ORGANISING
STUDY TIME
- Create an assignment calendar
- Prepare a running list
- Use daily”to do”list
OPTIMISING STUDY TIME
- Consider credit load
- Consider the difficulty level of classes
- Consider grade goals
- Learnt how long it takes to do assignments
- Monitor current study time
USING
TIME MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES TO STAY MOTIVATED
- Study in one hour blocks
- Take breaks
- Tackle difficult assignments first
- Switch subjects
- Break tasks down
- Work ahead
- Plan rewards
REDUCE
PROCRASTINATION
- Procrastination,is the act of putting off intentionally the doing of something that should be done
MAIN CAUSES OF
PROCRASTINATION
JOB TASK
ANALYSIS
MODULE 3
AT AL-BIRUNI 1
21/6/2017
MEMORY, LEARNING & IMPROVING CONCERNTRATION
BY:PUAN ROHANA BINTI
WAN ENDUT
·
Be reasonable
·
Memory
·
The size of the human
brain is three times greater than the size of the gorilla brain
What is in the brain?
Brain analyzed
·
Scan Magnetic reasoning Imaging
(MRI).
·
Can
measure brain electrical activity and brain function on certain parts
identified
Get
to know your brain
· Our brain manages data all the time.
· The brain transmitted data messages with speeds up
to 250km / h, by trillion cell networks.
· The brain can produce 25 watts of electricity which
is sufficient to turn on a bulb
· Flies have 100000 brain cells, mice have 5 million,
10 million monkeys and human brain have as much as 1 trillion brain cells.
· The right brain capacity is 100 times the left
brain. Some humans only use 3%, 97% stored in the right brain of the
unconscious part.
“The
Power of Mind 1: Setting Mind”
BLUE YELLOW BLACK
RED BLUE ORANGE
GREEN PURPLE RED
BLACK RED ORANGE
GREEN
BLUE BLACK
RED
PURPLE YELLOW
Our brain is trying to read the color, but our right brain will still read his writings
Memory
VS Brain
- Memory is an individual's ability to
store, maintain and remember information and experience.
- The brain is the organ.
Brain and memory association
- Analogy like a computer.
- Give
examples of the components that exist on a computer and whether the
components of the computer are as though it were in humans
- Eye
like Camera
- Mouth
like Speaker
Memory
- The human memory system is divided into
three types: sensory memory (SM), short term memory (STM) and long term
memory (LTM).
- Many are wondering how to improve one's
memory.
- But many do not understand or lack of
exposure about the nature of memory
Sensory
Memory (SM)
·
Memory
related to the storage of temporary information carried by the senses (5
senses).
·
Is
temporary.
·
If the attention of
the information will be processed into the Short-Term Memory (STM).
·
If it does not pay
attention the information is lost immediately.
Short-Term
Memory (STM)
·
STM is a process
that allows information to be received and stored within a short period of
between 30 seconds to 24 hours. Memory from SM.
·
This
is due to limited storage of information storage. Some information in the
short-term memory system will enter the long-term memory system provided
passengers and repeats.
·
The
information in the short-term memory will only be deleted / lost.
Recall
·
The disadvantage to
call back information stored in long-term memory is synonymous with forgotten words.
·
The genius and the
remarkable memory is the person who is capable of "recalling" the
information stored in the long-term memory system, if it is to be geius, the
potential of the brain to be strengthened by stimulating, training, nourishing,
maintaining and invigorating the brain through modern and traditional methods.
Memory
·
Brain development
can be enhanced through various stimuli, advice, exercise, training and
practice. Spirituality including prayer, taqwa and ibadah can nourish and
activate brain cells.
·
A healthy body
guarantees an intelligent brain.
Forget
& Remember
· Why
often forget:
v Disturbance
v Focus attention
v Time factor
·
Easy to remember if:
v Interest
v Choice
v Repeat
v Exercise
Elaboration Strategies
·
Acronyms / cacthwords
e.g: MAS – Malaysian Airline System
UiTM – Universiti
Teknologi MARA
·
Acronyms / cacthphrases
e.g: Carnivores – animal eaters
Herbivores – plant eaters
Omnivores – animal and plant eaters
Decomposes – eat decaying organisms
the Catchphrase: “Can Henry Omit Dents”
Mnemonics
·
Memory tricks.
·
Make it funny.
·
There
are two types of acronyms & rhythms
e.g. Micheal Jackson Kill His Brother In University
(M – merah, J – jingga, K – kuning, H – hijau, B –
biru, I – indigo, U – ungu)
Causes of Poor
Concentration
·
Lack
of attention.
·
Lack
of interest.
·
Lack
of motivation.
·
Distraction
from others.
·
Uncomfortable
environment.
·
Physiological
matters – illness, tiredness.
·
Physiological
matters – personal problems, worried, anxieties.
Strategies For
Improving Concentration
·
Use
motivational and organizational strategies – create interest in the work,
develop a positive attitude toward you work, use goal setting strategies, use
time management strategies.
·
Create
a positive learning environment – find a better location, reduce multitasking,
minimize distractions.
·
Deal
with internal distractions – deal with personal problems, deal with competing
activities.
·
Use
active learning strategies (as discussed in improving memory)
·
Match
your learning style to the task.
SQ3R: Survey,
Question, Read, Recite, Recite &
Review
· Read
v Read the paragraph for information
v Find answers from the questions that have been
constructed / formed. It helps students focus on reading
· Recite
v Summarize
v Make a short note and try to remember
v Remember and memorize important content
v Do exercises
· Review
v Review
v Memorize the contents in the note
v Try to recall the built-in questions and answer
them again
WEEK 4
TAKING LECTURE NOTES
AT
AT-TABARI HALL
5/7/2017
BY: SIR AHMAD FARIZ , MISS NOR SURIA & MADAM ROZITAMUHAMMAD
WHAT
IS TAKING NOTES?
Ø Writing down ideas from lecturers and readings in our own words
WHY
TAKE NOTES?
Ø Help us to pay attention
Ø Help us to engange our senses
Ø Help us take ownership of ideas
Ø Help us improve our memory
WHY
REVIEW NOTES
Ø We lose 80% of what we hear if it is not reviewed within a few
hours
Ø There is not enough time to absorb
Ø All the information given in class if it’s not reviewed on a
regular basic
WHY RECAPTURE
NOTES AFTER CLASS?
Ø Frees you up to write in quick,short hand during class
BEFORE
CLASS I WILL:
Ø Review the notes from the day before
Ø Review your reading assignment
Ø Write the date at the top of your paper for notes
PHSYCAL
FACTORS
Ø Seating near the front
Better vision
Better hearing
Ø Avoid distraction
Doorways,windows glare
How
do we takes notes
Ø Date and label notes
Ø Gave ourselves space to write
Ø Yse abbreviations and symbols
Use
an outline to show
Ø Main idea
Ø Supports
Ø Examples
Ø Use your own language
How
do we prepare for class?
Ø Do pre-reading and homework
Ø Review syllabus
Ø Preview previous notes
Ø Look up keywords prior to class
Ø Plan on listening 80% of the
fine
Ø Write the date of the top of your for notes
Ø Leaves spaces between the lines so that you can add information
later
While
taking notes
Ø Be an aggressive not a passive listener
Ø Ask questions and disccuss if its permitted
Ø If not ,jot question in you notes
Ø Seek out meaning
Benefits
if you sit in front
Ø It’s hard for you to fall asleep
Ø Lecturer can see you easily
Ø It’s easier to see the writing on the boards
Ø It’s tell lecturer that you declare willingness and ready to learn
Cornell
note taking
Ø Column method
Ø Mapping method
Ø Outlining
Ø Sentence method
How
to review back offer class
Ø Create some examples
Ø Rewrite
Ø Discuss with others and compare it
Ø Review note
Ø Practice those skills
Ø Ask the professor for certification
Ø Survey
Ø Question
Ø Read
Ø Ritte
Ø Review
Ø Recite
MODULE
5
AT
DEWAN KULIAH 2
12/7/2017
ACADEMIC
INTEGRITY & PERFOMANCE
BY:MOHD
IKHSAN BIN MOHD
RAUS
:ROSLAN JAMALUDDIN
:MOHD FAIZAL AZRUL
AZWAN MUHAMMED

WHAT
IS PLAGIARISM?
·
Plagiarism
is an actof using or closely imitating the language and thoughts of another
author without authorization and the representation ot that author’s work as
one’s own as by not crediting the original author.
AVOIDING
PLAGIARISM
PARAPHRASING
|
REFERENCING
|
·
Express the
meaning of the writer or speaker or something(written or spoken) usingba
different word especially to achieve greater clarity
|
·
Provide a
book or article with citations of authorities
|
STEPS
·
Rewards:replace
the words by synonyms
·
Change the
form of the sentence:active to passive
·
Make sure the
meaning is same
|
STEPS
·
Include a
“reference page” or page of of workcited at the end of paper
·
Check the
guidelines for citing sorces properly
·
Look for the
APA 6th formatting style
·
Refer to my
instructor lecturer
|
PREVETING
PLAGIARISM
PLANNING MY PAPER
|
||
1.Consult my instructor or lecturer
|
2.Plan my paper
|
3.Take effective notes
|
CALCULATING
GRADE POINT AVERAGE
GPA
·
Calculated
average of the letter grades a student earn in each semester following 0 -4.0 scale
·
GPA=The
total credit values registered and attempted in the assessment
The total credit
units acquired in the same semester
CGPA
·
It
refers to overall GPA.This includes dividing the number of quality points
earned in all courses.
·
CGPA=The
total credit values registered and attempted in the assessment
The total credit units
acquired in all semester
GPA
CALCULATION
Letter grade
|
Percent Grade
|
4.0
Scale
|
A+
|
90-100
|
4.00
|
A
|
80-89
|
4.00
|
A-
|
75-79
|
3.67
|
B+
|
70-74
|
3.33
|
B
|
65-69
|
3.00
|
B-
|
60-64
|
2.67
|
C+
|
55-59
|
2.33
|
C
|
50-54
|
2.00
|
C-
|
47-49
|
1.67
|
D+
|
44-46
|
1.33
|
D
|
40-43
|
1.00
|
E
|
30-39
|
|
F
|
0-29
|
0.00
|
GPA
WORKSHEET
1.Calculate
the GPA for Amelia Amer for her first semester.
Course and grade(1st
semester)
|
Course Point
Average
|
Comparative Animal Physiology:B+
|
=3.33 x3
=9.99
|
Biochemistry 1:C-
|
=1.67 x 4
=6.68
|
Integrated Physiology Lab:
|
=4.00 x 1
=4.00
|
Asian Civilization 1:
|
=1.67 x 3
=5.01
|
Ecology:
|
=4.00 x 3
=12.00
|
Korean 1:
|
=3.00 x 3
=9.90
|
Total number of credits
|
=17
|
Total Points Earned
|
=46.68
|
GPA
|
=46.68
17
=2.75
|
2.Calculate
what would have happened if Amelia had earned a B in Chemistry.
Chemistry:B(3.00),4 Credits
Total numbers of credits=17
Totals points earned =(3.33 x 3)+(3.00 x 4)+(4.00 x 1)+(1.67
x 3)+
(4.00 x 3)+(3.00 x 3)
=52.00
17
=3.06
3.What
is the difference in GPA?
=3.06-2.75
=0.31
4.Now
calculate Amelia GPA for the next semester:
Course and Grade(2nd
semester)
|
Course point average
|
Cell biology :B+
|
=3.33 x 4
=13.32
|
Organic Chemistry 1:B
|
=3.00 x 4
=12.00
|
Intro Physics 1:C
|
=2.00 x 4
=8.00
|
Public Speaking:A-
|
=3.67 x 3
=11.01
|
Writing in Biology:C
|
=2.00 x 3
=6.00
|
Total numbers of credit
|
=18
|
Total points earned
|
=50.33
|
GPA
|
18
=2.80
|
5.What
would happen if Amelia had received a D in
Cell Bio instead of the B+?
Cell
Bio =D(1.00),4
Credits
Total
number of credits=18
Total
points earned =(1.00 x 4)+(3.00 x
4)+(2.00 x 4)+(3.67 x3)+(2.00 x 3)
=41.01
18
=2.28
6.What
is difference in GPA?
=2.80-2.28
=0.52
7.What
is the difference in CGPA?
Points
earned :1st semester =46.68
:2nd semester
=50.33
97.01
Numbers
of credits:1st semester =1.7
;2nd
semester=18
35
35
=2.77
MODULE 6
AT DEWAN IBN HAZM
19/7/2017
GOAL SETTING
BY:PUAN HAMIDAH ABDUL
RAHMAN
: PUAN
ROSENANI SIDEK
WHAT ARE
GOALS?
In my opinion,goals are the ends
toward which direct our effort
My goals are:
·
Achieve
dean list for each semester
·
Graduate
CHARACTERISTIC
OF GOALS
·
Goals
should be positive
·
Goals
should be self-chosen
·
Goals
should be realistic
·
Goals
should be measurable
LONG AND SHORT-TERM GOALS
LONG-TERM GOALS
·
The objectives
we set for ourselves the end of the year,for four or five years from now or
even for lifetime
SHORT-TERM GOALS
·
It can be set
for an hour from now for the end of the day,week.month or term(or semester)
As
a example:things like completing a reading assignment,writing an essay,getting
a B in a course,getting off probation or making Dean’s list.
·
Think of my
short-term goals as step toward achieving the long-term goals I’ve set for
myself
ACADEMIC
AND PERSONAL GOALS
ACADEMIC GOALS
·
Relate
to my course work.They include things like going to class,completing
assignments and preparing for exams
PERSONAL GOALS
·
It
like making new friends,participating in clubs or sporting events,exercisingor
even doing my laundry
5
STEPS APPROACH TO SETTING GOALS
MODULE 7
AT AL-BUKHARI LIBRARY
26/7/2017
LIBRARY & CAMPUS
RESOURCES
BY:PUAN FARAWAHIDAH
BINTI
BADRUESHAM
:NOR FITRIAH BINTI MAT SEMAN
Type
Of Resources
Type of
resources
|
Example
|
UiTM Cawangan
Pahang,Kampus Jengka
|
Academic
Resources
|
Library, Information Technology &
Computer, Register
|
Al-Bukhari library, Administration
Building, Laboratory IT, HEA
|
Housing, Dining And Transportation
Resources
|
Buses, Dining Places
|
Station Bus, DM Kolej Tok Gajah,Tun
Fatimah, cooperative, Van, Bus
|
Student Organization Resources
|
Extra-curricular, Leisure Activities
|
HEP,
Rugby Field, Court, Stadium, Camp Gading
|
Al-Bukhari
Library Capacity
Reading Room
: 818 seats
Discussion Room
: 2 pieces (8 people/room)
Room IT : 80 computers
Training Room
: 36 seats
Total :
1030 seats
10 things Must Know About Al-Bukhari 1 &
2 Library
1.
Operation
Hours Al-Bukhari Library
Days
|
Time
|
Examination Season
|
Monday -
Friday
|
8.30 a.m. –
6.30 p.m.
|
8.30 a.m. –
10.50 p.m.
|
Saturday
|
9.30 a.m. –
6.30 p.m.
|
9.30 a.m. –
6.30 p.m.
|
Sunday
|
CLOSED
|
9.30 a.m. –
6.30 p.m.
|
2.
Loans
& Book Returns
User Category
|
(Open Shelf)
|
KBR
|
Reference
|
Magazine
|
||||
Total
|
Duration
|
Total
|
Duration
|
Total
|
Duration
|
Total
|
Duration
|
|
Degree Students
|
20
|
14 Days
|
2
|
2 Hours
|
Internal
Borrowing
|
Internal Borrowing
|
||
Diploma Students
|
20
|
14 Days
|
2
|
2 Hours
|
||||
Pre-students
|
20
|
14 Days
|
2
|
2 Hours
|
||||
3. Book
Loan & Return Book
Penalty
· If
the penalty is not paid, the next loan is not allowed.
RM0.20 Daily / A Copy
Book
Lost?
The Material Compensation Payment Process
v
Material
price.
v Cost
of sevice RM20.00.
v Penalty
@ change the same book title (latest edition).
v Pay late pass.
1.
|
If the required
book is not in the collection at Al-Bukhari library, loans to other
libraries can be applied at the main counter.
|
2.
IT Room Usage
|
IT Room
|
IT Room 1 : 60 PC IT Room 2 : 20 PC
·
PROHIBITED
TO ENTER SOFTWARE
·
PROHIBITED
TO STEAL EQUIPMENT & DEVICES COMPUTER
·
PROHIBITED
TO ACCESS TO PORN SITES
3.
Zone
In Library
1. Zone
Relax
·
Discussions can
be done in a relaxed
2. Zone
Quiet
·
Slow down your
voice
·
Ordinary
conversations are allowed in controlled tone
·
Set the handset
in silent mode
3. Zone
Silent
·
Any
conversations are not allowed
·
Mobile Phone
usage is not allowed
·
Everything was
silent
4.
i-Book
KKM
The module to be trained is :
· End Notes Software
· Online Databases
· Research Work
5.
URL
1. FACEBOOK
AL-Bukhari Library (http://www.facebook.com/puitmpahang)
2. Website
Al-Bukhari Library
(http://library.pahang.uitm.edu.my.v1.index.php)
3. Blog
Al-Bukhari Library
How
To Read Book?
·
Table of content
·
Index
·
Back of the book
/ summary
Let’s
Do Activity NOW!
1. Choose
5 books per group
2. Fulfill
the form
3. Read
book correctly and identify ;
·
Call Number
·
Table of content
·
Index
What
is APA Style?
·
APA (America
Psychological Association) style is most commonly used to cite sources with
within social sciences.
·
APA Style
originated in 1929, when a group of psychologists, anthropologists, and
business managers convened and sought to establish a simple set of procedures,
or style rules, that would codify the many components of scientific writing to
increase the ease of reading comprehension.
·
As with other
editorial styles, APA Styles cinsits of rules or guidelines that a publisher
observes to ensure clear and consistent presentation of written material. It
concerns inform use of such elements as :
v Selection
of heading, tone, and length;
v Presention
of numbers and statistics;
v Construction
of tables and figures;
v Citation
of references;
v Many
other elements that are a part of a manuscript.
·
APA Style rules
and guidelines are found in the sixth edition of the Publication Manual of the
America Psychological Association.
References:
Van Blerkom, D.L. (2009). Collage Study Skills:
Becoming a strategic learner (6th ed.).MA: Wadsworth Cengage Learning.
Publication manual of the America Psychological
Association (2010). (6th ed.). Washington,
D.C.: America Psychological Association.









Comments
Post a Comment